LANZHOU, Nov. 21 (Xinhua) -- Chinese researchers have proposed the potential of applying probiotics in health care, releasing a systematic review of their action mechanism, according to Lanzhou University.
The study sheds light on the application of probiotics, prebiotics and postbiotics in disease treatment, and opens new frontiers in probiotics research, the university said.
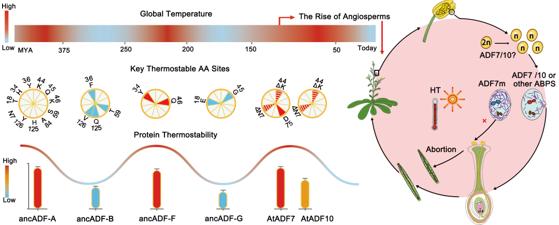
The gut microbiota and its homeostasis play crucial roles in human health. Existing medicines can relieve symptoms for some diseases related to the gut microbiota, but they are unable to solve the root causes or even the main side effects, said Li Xiangkai, a professor at Lanzhou University's School of Life Sciences.
Growing numbers of clinical studies and mounting evidence have demonstrated that probiotics, prebiotics and postbiotics can prevent and treat various diseases, but they can only be used as dietary supplements at present, rather than as medicines, Li said.
Researchers from Lanzhou University, Shandong University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Institute of Microbiology worked together to conduct the study by analyzing the importance of the gut microbiota in human health and the problems faced by existing medicines.
They systematically summarized the effectiveness and mechanisms of probiotics, prebiotics and postbiotics in maintaining health and treating diseases.
The researchers also analyzed the challenges to and prospects of such clinical application in maintaining health and alleviating and treating diseases, and proposed the concept of "probacine" for further exploration.
The results of the study have been published in the journal MedComm.